Payroll Advance: Powerful Ways to Enhance Workplace Morale
Employees sometimes undergo surprising financial crises, acute medical situations, vehicle repairs, or family crises that require urgent access to cash. In these situations, waiting until the next payday can be difficult and problematic. This is where the concept of payroll advance comes in.
A payroll advance allows employees to obtain a portion of their upcoming salary or compensation before the scheduled payday. It is a significant benefit that can overcome employee stress and improve workplace satisfaction, but it must be directed properly by employers to avoid any financial complications.
In this article, we will study what a payroll advance is, how it works, its pros and cons, compliance requirements, and best practices for employers.

What is a Payroll Advance?
A “payroll advance,” also called a salary advance or wage advance, is an agreement between an employer and employee, where an employer allows an employee to obtain a portion of their future salary before the scheduled pay date. It is primarily a prepayment of wages, the employee has earned or is expected to earn in the near future but has not yet received.
Key Characteristics
- Normally deducted from the employee’s upcoming salary.
- Generally interest-free, but may charge a small administrative fee.
- Commonly used for extreme emergencies or urgent financial requirements.
- It is considered a short-term financial solution, not a long-term agreement.
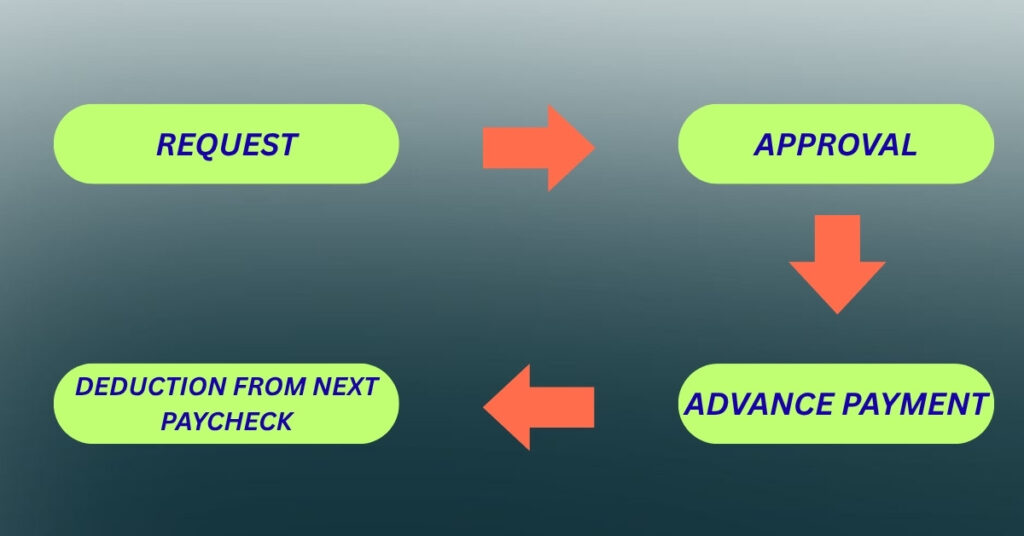
How Does Payroll Advance Work?
The process to get a payroll advance varies from company to company, but a few general steps are:
Employee Request:
The employee officially requests an advance, also mentioning the reasons and the amount they need.
Employer Review:
The employer reviews the request of the employee based on company policy, also evaluates the employee’s pay history, and the criteria for eligibility.
Advance Disbursement:
If an employee’s request is approved, the employer provides the employee the requested amount via check, bank transfer, or cash.
Deduction at Payday:
The payroll advanced amount is to be deducted from the employee’s next salary or compensation.
Example
If an employee is due to receive their salary of $1,000 on payday but is given a $300 advance, their payment on payday will be reduced by $300, and the remaining $700 will be given on payday.
Types of Payroll Advance
There are commonly two types of payroll advances:
Earned Wage Advance (EWA)
This is the most common type of advance, and employees can obtain their salaries or wages that they have already earned during the current pay period, but they have not yet been paid.
- Example: If an employee has worked 40 hours till now and payday is still five days away, they can request formally for an advance on the wages for those 40 hours.
Future Wage Advance (FWA)
In this type of advance, employees are allowed to obtain their wages they have not yet earned. This method is not in common use because it assumes a higher financial risk for the employer.
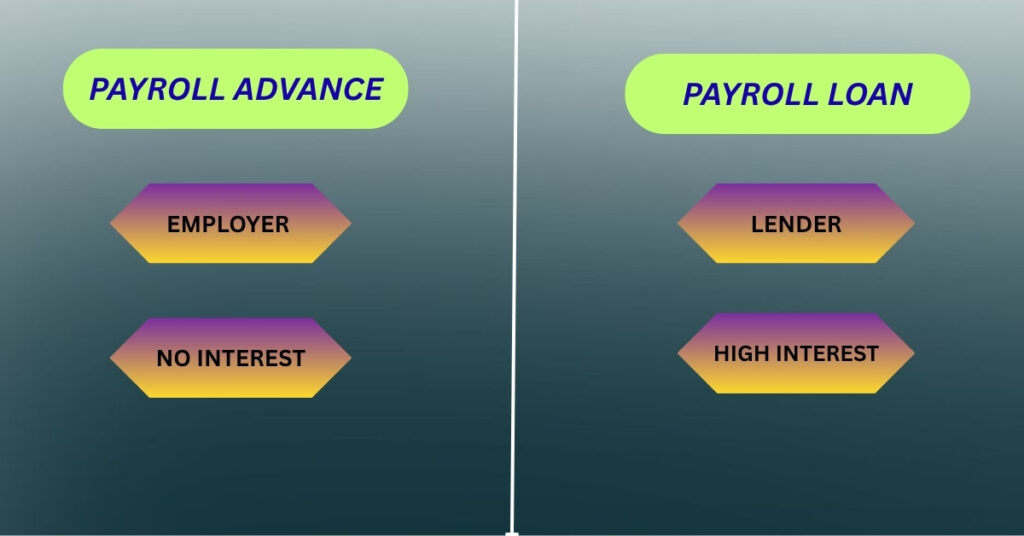
Payroll Advance vs Payday Loans
It is most important to differentiate payroll advances from payday loans.
| Feature | Payroll Advance | Payday Loan |
| Provider | Employer | External lender |
| Interest/Fees | Typically no interest, may have a small fee | High interest and fees |
| Repayment | Deducted from upcoming paycheck | Must repay separately |
| Impact on Employee | Low cost, employer-controlled | Can lead to debt cycles |
Why Do Employees Request Payroll Advances?
Employees usually request payroll advances for their financial emergencies or to fulfill urgent requirements. Common reasons may include:
- Medical bills or family emergencies
- Car / Van repairs
- Utility bills or rent payments
- Random home repairs
- Avoiding high-interest
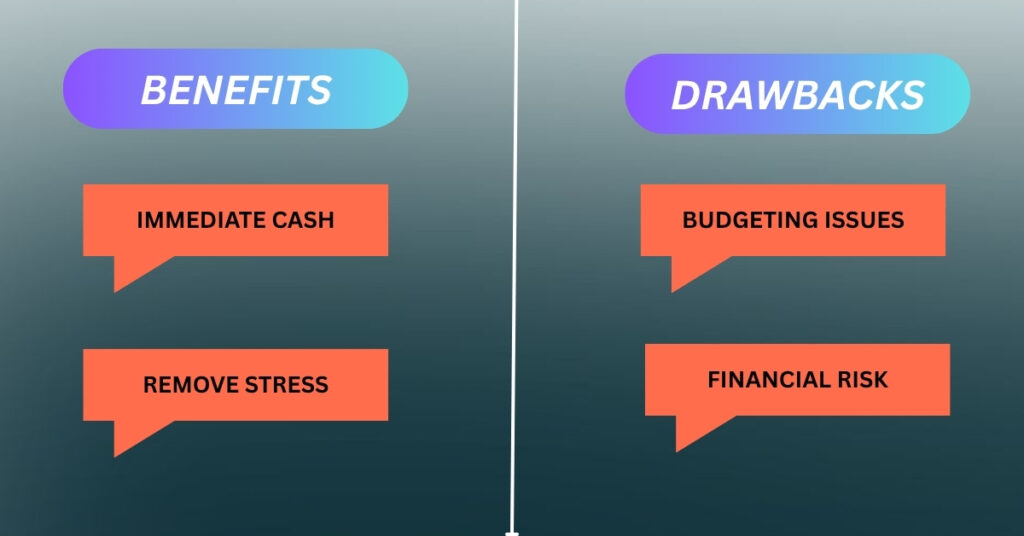
Benefits of Payroll Advances
For Employees
- Gives immediate access to requested cash during emergencies.
- Helps to overcome stress and financial anxiety.
- In order to avoid high-interest on loans or credit card debt.
- It can enhance employee morale and loyalty to the employer/company.
For Employers
- Improve employee satisfaction, loyalty, and retention in the company.
- Represent the employer’s dedication to employee well-being.
- It may enhance productivity by reducing employee crises caused by financial challenges.
Drawbacks of Payroll Advances
For Employees
- May lead to dependence if used frequently.
- It can create budgeting challenges due to deductions from the paycheck on payday.
For Employers
- More administrative burden to manage payroll advance requests.
- There is a risk of financial loss if the employee leaves before repaying the total amount of the advance.
- It can disturb the company’s cash flow if too many advances are given to employees.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Local labor law must be followed by the employer while offering payroll advances. Key legal considerations may include:
- Document the arrangement: Requested amount, valid reasons, and repayment terms should be part of the written agreement.
- No excessive deductions: Deductions from the paycheck must comply with the local law of the region in which the agreement was made.
- Tax implications: Payroll advances are typically not taxable at the time of the advance but must be recorded in the payroll record for proper reflection in financial statements.
- Fairness and non-discrimination: Employers must follow the same policy consistently for all employees for the payment of the requested amount of advances.
How to Implement a Payroll Advance Policy
Provide Clear Guidelines
- Eligibility criteria must be defined for payroll advance requests (e.g., part-time employees, full-time employees, minimum tenure).
- Set a maximum advance limit of payroll advance (e.g., 50% of the upcoming paycheck).
- Determine how many times employees can request advances (e.g., once every six or twelve months).
Document the Process
- Require employees to submit a written request in order to get approval for an advance.
- A written agreement must be signed by both for repayment purposes.
Automate Where Possible
Try to use payroll software for tracking advances and automatically deduction repayments from the next paycheck of employees.
Communicate Transparently
Employees must fully acknowledge how payroll advances work, including any fees or impact on future paychecks.
Alternatives to Payroll Advances
Many employers also offer other solutions instead of payroll advances, including:
- Earned Wage Access (EWA) Platforms: With the help of these platforms, employees can obtain their earned wages immediately using third-party apps.
- Short-term employee loans: Employers also provide structured loans with clear repayment terms and conditions, managing their cash flow too in order to avoid any financial discrepancy.
- Financial wellness programs: These programs are conducted to help employees for their budgets and plan expenses.
Best Practices for Employers
- Must limit payroll advances to overcome true emergencies of their employees.
- Tracking of payroll advances must be in practice using payroll software.
- Disseminate all information to employees about responsible usage.
- Conduct periodic checks to determine the impact of policy on cash flow and employee satisfaction.
Conclusion
Payroll advances can be helpful for employees by giving them financial relief during difficult times. If it is executed with clear guidelines and is recorded properly for accounting purposes, then employers can improve employee loyalty and satisfaction.
However, both employers and employees must use these advances transparently and ethically. Employers should formulate a transparent policy, ensure compliance with the region’s labor laws, and give alternatives to employees, such as earned wage access platforms, for more flexibility and timely repayment of advances.
By implementing a payroll policy with financial discipline, employers can make payroll advances a very helpful and sustainable solution for their employees.

Related Articles:
- Powerful Mobile Marketing Strategies You Must Try
- Best Marketing Tools In An Advertising Plan
- Mastering Revenue Expenditure for Business Success
- Market Research And Its Importance: A Comprehensive Review
- What You Should Know? Notes Payable And Accounts Payable
- Digital Marketing And Strategies: A Comprehensive Review with Examples
- Are Annuities the Best Investment for a Bright Future? A Comprehensive Analysis
- Understanding Capital Expenditure: Definition, Significance, and Its Association in Financial Decision-Making
- Difference Between Accounting And Finance: A Proven Comprehensive Guide For Beginners
- Difference between Annuity due and Ordinary Annuity
- Essential Accounting Software for Small Enterprises







